OCTG Pipes are mainly used for drilling oil and gas wells and transporting oil and gas. It includes oil drill pipes, oil casings, and oil extraction pipes. OCTG Pipes are mainly used to connect drill collars and drill bits and transmit drilling power.Petroleum casing is mainly used to support the wellbore during drilling and after completion, to ensure the normal operation of the entire oil well during the drilling process and after completion. The oil and gas at the bottom of the oil well are mainly transported to the surface by the oil pumping tube.
Oil casing is the lifeline for maintaining the operation of oil wells. Due to different geological conditions, the stress state underground is complex, and the combined effects of tension, compression, bending, and torsion stress on the casing body pose high requirements for the quality of the casing itself. Once the casing itself is damaged for some reason, it may lead to a reduction in production or even scrapping of the entire well.
According to the strength of the steel itself, the casing can be divided into different steel grades, namely J55, K55, N80, L80, C90, T95, P110, Q125, V150, etc. The steel grade used varies depending on the well condition and depth. In corrosive environments, it is also required that the casing itself has corrosion resistance. In areas with complex geological conditions, it is also required that the casing has anti collapse performance.
I.the basic knowledge OCTG Pipe
1、Specialized terms related to petroleum pipe explanation
API: it is the abbreviation of American Petroleum Institute.
OCTG: It is the abbreviation of Oil Country Tubular Goods, which means oil-specific tubing, including finished oil casing, drill pipe, drill collars, hoops, short joints and so on.
Oil Tubing: Tubing used in oil wells for oil extraction, gas extraction, water injection and acid fracturing.
Casing: Tubing that is lowered from the surface of the earth into a drilled borehole as a liner to prevent the collapse of the well wall.
Drill pipe: Pipe used for drilling boreholes.
Line pipe: Pipe used to transport oil or gas.
Circlips: Cylinders used to connect two threaded pipes with internal threads.
Coupling material: Pipe used for manufacturing couplings.
API Threads: Pipe threads specified by API 5B standard, including oil pipe round threads, casing short round threads, casing long round threads, casing offset trapezoidal threads, line pipe threads and so on.
Special Buckle: Non-API threads with special sealing properties, connection properties and other properties.
Failure: deformation, fracture, surface damage and loss of original function under specific service conditions. The main forms of oil casing failure are: extrusion, slippage, rupture, leakage, corrosion, bonding, wear and so on.
2、Petroleum related standards
API 5CT: Casing and Tubing Specification (currently the latest version of the 8th edition)
API 5D: Drill pipe specification (the latest version of the 5th edition)
API 5L: pipeline steel pipe specification (the latest version of the 44th edition)
API 5B: Specification for machining, measuring and inspection of casing, oil pipe and line pipe threads
GB/T 9711.1-1997: Technical conditions for delivery of steel pipes for transportation of oil and gas industry Part 1: Grade A steel pipes
GB/T9711.2-1999: Technical conditions of delivery of steel pipes for the transportation of oil and gas industry Part 2: Grade B steel pipes
GB/T9711.3-2005: Technical Conditions of Delivery of Steel Pipes for the Transportation of Petroleum and Natural Gas Industry Part 3: Grade C Steel Pipe
Ⅱ. Oil pipe
1. Classification of oil pipes
Oil pipes are divided into Non-Upset (NU) tubing, External Upset (EU) tubing, and integral joint tubing. Non-Upset tubing refers to a pipe end that is threaded without thickening and equipped with a coupling. External Upset tubing refers to two pipe ends that have been externally thickened, then threaded and fitted with clamps. Integrated joint tubing refers to a pipe that is directly connected without a coupling, with one end threaded through an internally thickened external thread and the other end threaded through an externally thickened internal thread.
2.The role of tubing
①, extraction of oil and gas: after the oil and gas wells are drilled and cemented, the tubing is placed in the oil casing to extract oil and gas to the ground.
②, water injection: when the downhole pressure is not enough, inject water into the well through the tubing.
③, Steam injection: In the process of thermal recovery of thick oil, steam is to be input to the well with insulated oil pipes.
(iv) Acidizing and fracturing: In the late stage of well drilling or in order to improve the production of oil and gas wells, it is necessary to input acidizing and fracturing medium or curing material to the oil and gas layer, and the medium and curing material are transported through the oil pipe.
3.Steel grade of oil pipe
The steel grades of oil pipe are: H40, J55, N80, L80, C90, T95, P110.
N80 is divided into N80-1 and N80Q, the two are the same tensile properties of the same, the two differences are the delivery status and impact performance differences, N80-1 delivery by normalized state or when the final rolling temperature is greater than the critical temperature Ar3 and tension reduction after air cooling, and can be used to find alternatives to normalizing hot-rolled, impact and non-destructive testing is not required; N80Q must be tempered (quenching and tempering) Heat treatment, impact function should be in line with the provisions of API 5CT, and should be non-destructive testing.
L80 is divided into L80-1, L80-9Cr and L80-13Cr. Their mechanical properties and delivery status are the same. Differences in use, production difficulty and price, L80-1 for the general type, L80- 9Cr and L80-13Cr are high corrosion resistance tubing, production difficulty, expensive, usually used for heavy corrosion wells.
C90 and T95 are divided into type 1 and type 2, that is, C90-1, C90-2 and T95-1, T95-2.
4.Commonly used steel grade, grade and delivery status of oil pipe
Steel grade grade Delivery status
J55 oil pipe 37Mn5 flat oil pipe: hot rolled instead of normalized
Thickened oil pipe: full-length normalized after thickening.
N80-1 tubing 36Mn2V Flat-type tubing: hot-rolled instead of normalized
Thickened oil pipe: full-length normalized after thickening
N80-Q oil pipe 30Mn5 full-length tempering
L80-1 oil pipe 30Mn5 full-length tempering
P110 oil pipe 25CrMnMo full-length tempering
J55 coupling 37Mn5 hot rolled on-line normalization
N80 coupling 28MnTiB full-length tempering
L80-1 coupling 28MnTiB full-length tempering
P110 Clamps 25CrMnMo Full Length Tempered

Ⅲ. Casing
1、Categorization and role of casing
Casing is a steel pipe that supports the wall of oil and gas wells. Several layers of casing are used in each well according to different drilling depths and geological conditions. Cement is used to cement the casing after it is lowered into the well, and unlike oil pipe and drill pipe, it cannot be reused and belongs to disposable consumable materials. Therefore, the consumption of casing accounts for more than 70% of all oil well tubing. Casing can be categorized into: conduit, surface casing, technical casing and oil casing according to its use, and their structures in oil wells are shown in below picture.
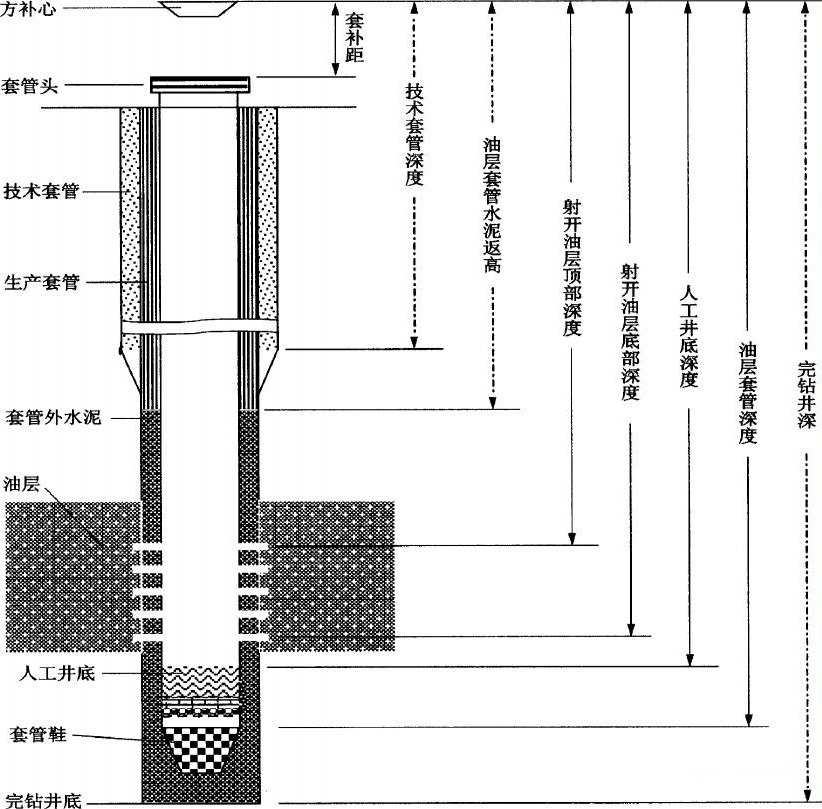
2.Conductor casing
mainly used for drilling in the ocean and desert to separate seawater and sand to ensure the smooth progress of drilling, the main specifications of this layer of 2.casing are: Φ762mm(30in )×25.4mm, Φ762mm(30in)×19.06mm.
Surface casing: It is mainly used for the first drilling, drilling open the surface of the loose strata to the bedrock, in order to seal this part of the strata from collapsing, it needs to be sealed with the surface casing. The main specifications of surface casing: 508mm (20in), 406.4mm (16in), 339.73mm (13-3/8in), 273.05mm (10-3/4in), 244.48mm (9-5/9in), etc. The depth of the lowering pipe depends on the depth of the soft formation. The depth of the lower pipe depends on the depth of the loose stratum, which is generally 80~1500 m. Its external and internal pressure is not large, and it generally adopts K55 steel grade or N80 steel grade.
3.Technical casing
Technical casing is used in the drilling process of complex formations. When encountering complex parts such as collapsed layer, oil layer, gas layer, water layer, leakage layer, salt paste layer, etc., it is necessary to put down the technical casing to seal it, otherwise the drilling can not be carried out. Some wells are deep and complex, and the depth of the well reaches thousands of meters, this kind of deep wells need to put down several layers of technical casing, its mechanical properties and sealing performance requirements are very high, the use of steel grades are also higher, in addition to K55, more is the use of N80 and P110 grades, some deep wells are also used in the Q125 or even higher non-API grades, such as V150. the main specifications of the technical casing are: 339.73 The main specifications of technical casing are as follows: 339.73mm(13-3/8in), 273.05mm(10-3/4in), 244.48mm(9-5/8in), 219.08mm(8-5/8in), 193.68mm(7-5/8in), 177.8mm(7in) and so on.
4. Oil casing
When a well is drilled to the destination layer (the layer containing oil and gas), it is necessary to use the oil casing to seal the oil and gas layer and the upper exposed strata, and the inside of the oil casing is the oil layer. Oil casing in all types of casing in the deepest well depth, its mechanical properties and sealing performance requirements are also the highest, the use of steel grade K55, N80, P110, Q125, V150 and so on. The main specifications of formation casing are: 177.8mm(7in), 168.28mm(6-5/8in), 139.7mm(5-1/2in), 127mm(5in), 114.3mm(4-1/2in), etc. The casing is the deepest among all kinds of wells, and its mechanical performance and sealing performance are the highest.

V.Drill pipe
1、 Classification and role of pipe for drilling tools
The square drill pipe, drill pipe, weighted drill pipe and drill collar in drilling tools form the drill pipe. The drill pipe is the core drilling tool that drives the drill bit from the ground to the bottom of the well, and it is also a channel from the ground to the bottom of the well. It has three main roles: ① transferring torque to drive the drill bit to drill; ② relying on its own weight to exert pressure on the drill bit to break the rock at the bottom of the well; ③ conveying the well washing fluid, that is, the drilling mud through the ground through the high-pressure mud pumps, into the borehole of the drilling column to flow into the bottom of the well to flush the rock debris and cool the drill bit, and carry the rock debris through the annular space between the outer surface of the column and the wall of the well to return to the ground, so as to achieve the purpose of drilling the well. Drill pipe in the drilling process to withstand a variety of complex alternating loads, such as tensile, compression, torsion, bending and other stresses, the inner surface is also subject to high-pressure mud scouring and corrosion.
(1) square drill pipe: square drill pipe has two kinds of quadrilateral type and hexagonal type, China's oil drilling rod each set of drill column usually use a quadrilateral type drill pipe. Its specifications are: 63.5mm (2-1/2in), 88.9mm (3-1/2in), 107.95mm (4-1/4in), 133.35mm (5-1/4in), 152.4mm (6in) and so on. Usually the length used is 12~14.5m.
(2) Drill pipe: Drill pipe is the main tool for drilling wells, connected to the lower end of the square drill pipe, and as the drilling well continues to deepen, the drill pipe keeps lengthening the drill column one after another. The specifications of drill pipe are: 60.3mm (2-3/8in), 73.03mm (2-7/8in), 88.9mm (3-1/2in), 114.3mm (4-1/2in), 127mm (5in), 139.7mm (5-1/2in) and so on.
(3) Weighted Drill Pipe: Weighted drill pipe is a transitional tool connecting drill pipe and drill collar, which can improve the force condition of drill pipe as well as increase the pressure on drill bit. The main specifications of weighted drill pipe are 88.9mm (3-1/2in) and 127mm (5in).
(4) Drill collar: the drill collar is connected to the lower part of the drill pipe, which is a special thick-walled pipe with high rigidity, exerting pressure on the drill bit to break the rock, and can play a guiding role when drilling straight wells. The common specifications of drill collar are: 158.75mm (6-1/4in), 177.85mm (7in), 203.2mm (8in), 228.6mm (9in) and so on.

V. Line pipe
1、Classification of line pipe
Line pipe is used in the oil and gas industry for the transportation of oil, refined oil, natural gas and water pipelines with steel pipe for short. Transportation of oil and gas pipelines are mainly divided into the main pipeline, branch pipeline and urban pipeline network pipeline three kinds, the main pipeline transmission line of the usual specifications for ∮ 406 ~ 1219mm, wall thickness of 10 ~ 25mm, steel grade X42 ~ X80; branch pipeline and urban pipeline network pipeline of the usual specifications for # 114 ~ 700mm, wall thickness of 6 ~ 20mm, steel grade X42 ~ X80. The usual specifications for feeder pipelines and urban pipelines are 114-700mm, wall thickness 6-20mm, steel grade X42-X80.
Line pipe has welded steel pipe, also has seamless steel pipe, welded steel pipe is used more than seamless steel pipe.
2、Line pipe standard
Line pipe standard is API 5L "pipeline steel pipe specification", but China in 1997 promulgated two national standards for pipeline pipe: GB/T9711.1-1997 "oil and gas industry, the first part of the technical conditions of delivery of steel pipe: A-grade steel pipe" and GB/T9711.2-1997 "oil and gas industry, the second part of the technical conditions of delivery of steel pipe: B-grade steel pipe". Steel Pipe", these two standards are equivalent to API 5L, many domestic users require the supply of these two national standards.
3、About PSL1 and PSL2
PSL is the abbreviation of product specification level. Line pipe product specification level is divided into PSL1 and PSL2, can also be said that the quality level is divided into PSL1 and PSL2. PSL1 is higher than PSL2, the 2 specification level is not only a different test requirements, and the chemical composition, mechanical properties requirements are different, so according to API 5L order, the terms of the contract in addition to specify the specifications, steel grade and other common indicators, but also must indicate the product Specification level, that is, PSL1 or PSL2.
PSL2 in the chemical composition, tensile properties, impact power, non-destructive testing and other indicators are stricter than PSL1.
4、pipeline pipe steel grade and chemical composition
Line pipe steel grade from low to high is divided into: A25, A, B, X42, X46, X52, X60, X65, X70 and X80.
5, line pipe water pressure and non-destructive requirements
Line pipe should be done branch by branch hydraulic test, and the standard does not allow non-destructive generation of hydraulic pressure, which is also a big difference between the API standard and our standards.
PSL1 does not require nondestructive testing, PSL2 should be nondestructive testing branch by branch.

VI.Premium Connection
1、Introduction of Premium Connection
Special buckle is different from API thread with special structure of pipe thread. Although the existing API threaded oil casing is widely used in oil well exploitation, its shortcomings are clearly shown in the special environment of some oil fields: the API round threaded pipe column, although its sealing performance is better, the tensile force borne by the threaded part is only equivalent to 60% to 80% of the strength of the pipe body, so it can not be used in the exploitation of deep wells; the API biased trapezoidal threaded pipe column, the tensile performance of the threaded part is only equivalent to the strength of the pipe body, thus it can not be used in deep wells; API biased trapezoidal threaded pipe column, its tensile performance is not good. Although the tensile performance of the column is much higher than that of API round thread connection, its sealing performance is not very good, so it can't be used in the exploitation of high-pressure gas wells; in addition, the threaded grease can only play its role in the environment with the temperature below 95℃, so it can't be used in the exploitation of high-temperature wells.
Compared with API round thread and partial trapezoidal thread connection,Premium Connection has made breakthrough progress in the following aspects:
(1) good sealing, through the design of elastic and metal sealing structure, so that the joint gas sealing resistance to reach the limit of the tubing body within the yield pressure;
(2) high strength of the connection, with Premium Connection connection of the oil casing, the strength of the connection reaches or exceeds the strength of the tubing body, to solve the problem of slippage fundamentally;
(3) by the Material selection and surface treatment process improvement, basically solved the problem of thread sticking buckle;
(4) through the optimization of the structure, so that the joint stress distribution is more reasonable, more conducive to the resistance to stress corrosion;
(5) through the shoulder structure of the reasonable design, so that on the buckle operation is easier to carry out.
At present, the world has developed more than 100 kinds of Premium Connections with patented technology.
Post time: Feb-21-2024
