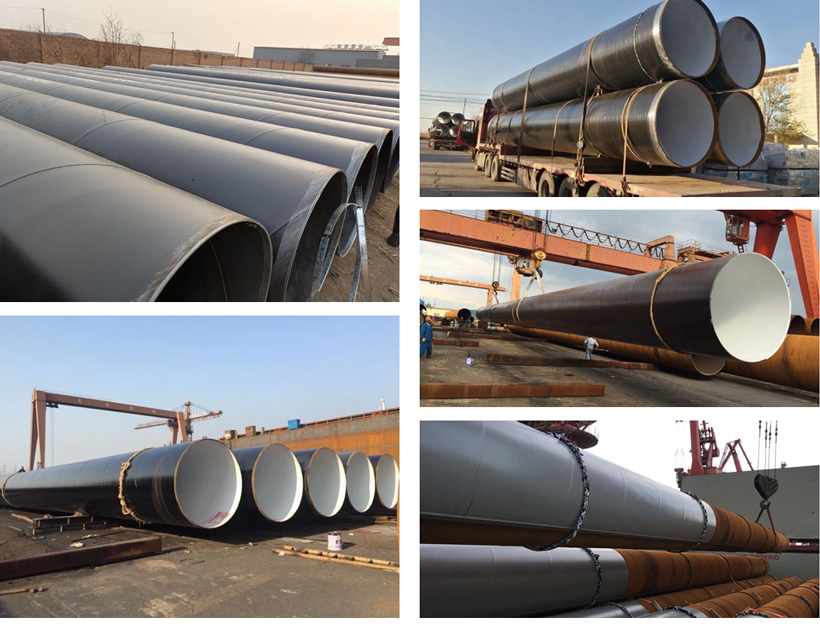
Product Description
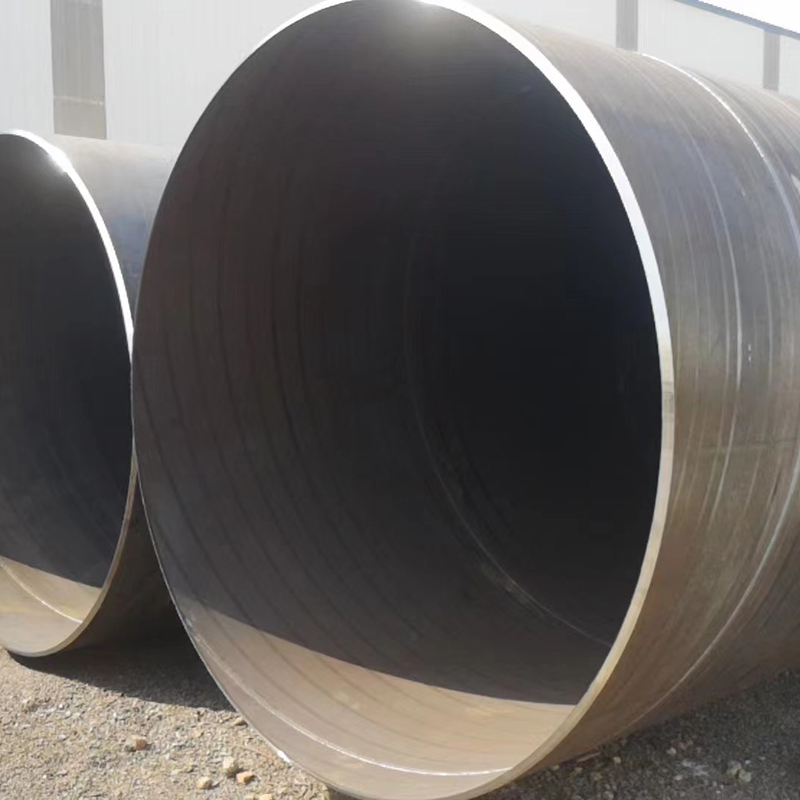
Spiral steel pipes, also known as helical submerged arc-welded (HSAW) pipes, are a type of steel pipe characterized by their distinctive manufacturing process and structural properties. These pipes are widely used in various industries due to their strength, durability, and adaptability. Here is a detailed description of spiral steel pipes:
Manufacturing Process: Spiral steel pipes are produced through a unique process involving the use of a coil of steel strip. The strip is unwound and formed into a spiral shape, then welded using the submerged arc welding (SAW) technique. This process results in a continuous, helical seam along the length of the pipe.
Structural Design: The helical seam of spiral steel pipes provides inherent strength, making them suitable for withstanding high loads and pressures. This design ensures uniform distribution of stress and enhances the pipe's ability to resist bending and deformation.
Size Range: Spiral steel pipes come in a wide range of diameters (up to 120 Inch) and thicknesses, allowing for flexibility in various applications. They are commonly available in larger diameters compared to other pipe types.
Applications: Spiral steel pipes are used in diverse industries such as oil and gas, water supply, construction, agriculture, and infrastructure development. They are suitable for both above-ground and underground applications.
Corrosion Resistance: To enhance longevity, spiral steel pipes often undergo anti-corrosion treatments. These can include internal and external coatings, such as epoxy, polyethylene, and zinc, which protect the pipes from environmental elements and corrosive substances.
Advantages: Spiral steel pipes offer several advantages, including high load-bearing capacity, cost-effectiveness for large-diameter pipes, ease of installation, and resistance to deformation. Their helical design also aids in efficient drainage.
Longitudinal VS Spiral: Spiral steel pipes are distinguishable from longitudinally welded pipes by their manufacturing process. While longitudinal pipes are formed and welded along the length of the pipe, spiral pipes have a helical seam formed during manufacturing.
Quality Control: Manufacturing and quality control processes are crucial in producing reliable spiral steel pipes. Welding parameters, pipe geometry, and testing methods are carefully monitored to ensure adherence to industry standards and specifications.
Standards and Specifications: Spiral steel pipes are manufactured in accordance with international and industry-specific standards such as API 5L, ASTM, EN, and others. These standards define material properties, manufacturing methods, and testing requirements.
In summary, spiral steel pipes are a versatile and durable solution for various industries. Their unique manufacturing process, inherent strength, and availability in different sizes contribute to their widespread use in infrastructure, transportation, energy,port construction and more. Proper selection, quality control, and corrosion protection measures play a crucial role in ensuring the long-term performance of spiral steel pipes.
Specifications
| API 5L: GR.B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70, X80 |
| ASTM A252: GR.1, GR.2, GR.3 |
| EN 10219-1: S235JRH, S275J0H, S275J2H, S355J0H, S355J2H, S355K2H |
| EN10210: S235JRH, S275J0H, S275J2H, S355J0H, S355J2H, S355K2H |
| ASTM A53/A53M: GR.A, GR.B |
| EN 10217: P195TR1, P195TR2, P235TR1, P235TR2, P265TR1, P265TR2 |
| DIN 2458: St37.0, St44.0, St52.0 |
| AS/NZS 1163: Grade C250 , Grade C350, Grade C450 |
| GB/T 9711: L175, L210, L245, L290, L320 , L360, L390 , L415, L450 , L485 |
| ASTMA671: CA55/CB70/CC65, CB60/CB65/CB70/CC60/CC70, CD70/CE55/CE65/CF65/CF70, CF66/CF71/CF72/CF73, CG100/CH100/CI100/CJ100 |
| Diameter(mm) | Wall Thickness(mm) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | |
| 219.1 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||||
| 273 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||||||
| 323.9 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||||
| 325 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||||
| 355.6 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||||
| 377 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| 406.4 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| 426 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| 457 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| 478 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| 508 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 529 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 630 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 711 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 720 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 813 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 820 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 920 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 1020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 1220 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 1420 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 1620 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 1820 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 2020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 2220 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| 2500 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 2540 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 3000 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
Tolerance of Outside Diameter and Wall Thickness
| Standard | Tolerance of Pipe Body | Tolerance of Pipe End | Tolerance of Wall Thickness | |||
| Out Diameter | Tolerance | Out Diameter | Tolerance | |||
| GB/T3091 | OD≤48.3mm | ≤±0.5 | OD≤48.3mm | - | ≤±10% | |
| 48.3<od≤273.1mm | ≤±1.0% | 48.3<od≤273.1mm | - | |||
| 273.1<od≤508mm | ≤±0.75% | 273.1<od≤508mm | -0.8~+2.4 | |||
| OD>508mm | ≤±1.0% | OD>508mm | -0.8~+3.2 | |||
| GB/T9711.1 | OD≤48.3mm | -0.79~+0.41 | - | - | OD≤73 | -12.5%~+20% |
| 60.3<od≤457mm | ≤±0.75% | OD≤273.1mm | -0.4~+1.59 | 88.9≤OD≤457 | -12.5%~+15% | |
| 508<od≤941mm | ≤±1.0% | OD≥323.9 | -0.79~+2.38 | OD≥508 | -10.0%~+17.5% | |
| OD>941mm | ≤±1.0% | - | - | - | - | |
| GB/T9711.2 | 60<od≤610mm | ±0.75%D~±3mm | 60<od≤610mm | ±0.5%D~±1.6mm | 4mm<wt | ±12.5%T~±15.0%T |
| 610<od≤1430mm | ±0.5%D~±4mm | 610<od≤1430mm | ±0.5%D~±1.6mm | WT≥25mm | -3.00mm~+3.75mm | |
| OD>1430mm | - | OD>1430mm | - | - | -10.0%~+17.5% | |
| SY/T5037 | OD<508mm | ≤±0.75% | OD<508mm | ≤±0.75% | OD<508mm | ≤±12.5% |
| OD≥508mm | ≤±1.00% | OD≥508mm | ≤±0.50% | OD≥508mm | ≤±10.0% | |
| API 5L PSL1/PSL2 | OD<60.3 | -0.8mm~+0.4mm | OD≤168.3 | -0.4mm~+1.6mm | WT≤5.0 | ≤±0.5 |
| 60.3≤OD≤168.3 | ≤±0.75% | 168.3<od≤610 | ≤±1.6mm | 5.0<wt | ≤±0.1T | |
| 168.3<od≤610 | ≤±0.75% | 610<od≤1422 | ≤±1.6mm | T≥15.0 | ≤±1.5 | |
| 610<od≤1422 | ≤±4.0mm | OD>1422 | - | - | - | |
| OD>1422 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| API 5CT | OD<114.3 | ≤±0.79mm | OD<114.3 | ≤±0.79mm | ≤-12.5% | |
| OD≥114.3 | -0.5%~1.0% | OD≥114.3 | -0.5%~1.0% | ≤-12.5% | ||
| ASTM A53 | ≤±1.0% | ≤±1.0% | ≤-12.5% | |||
| ASTM A252 | ≤±1.0% | ≤±1.0% | ≤-12.5% | |||
|
DN mm |
NB Inch |
OD mm |
SCH40S mm |
SCH5S mm |
SCH10S mm |
SCH10 mm |
SCH20 mm |
SCH40 mm |
SCH60 mm |
XS/80S mm |
SCH80 mm |
SCH100 mm |
SCH120 mm |
SCH140 mm |
SCH160 mm |
SCHXXS mm |
|
6 |
1/8” |
10.29 |
1.24 |
1.73 |
2.41 |
|||||||||||
|
8 |
1/4” |
13.72 |
1.65 |
2.24 |
3.02 |
|||||||||||
|
10 |
3/8” |
17.15 |
1.65 |
2.31 |
3.20 |
|||||||||||
|
15 |
1/2” |
21.34 |
2.77 |
1.65 |
2.11 |
2.77 |
3.73 |
3.73 |
4.78 |
7.47 |
||||||
|
20 |
3/4” |
26.67 |
2.87 |
1.65 |
2.11 |
2.87 |
3.91 |
3.91 |
5.56 |
7.82 |
||||||
|
25 |
1” |
33.40 |
3.38 |
1.65 |
2.77 |
3.38 |
4.55 |
4.55 |
6.35 |
9.09 |
||||||
|
32 |
1 1/4” |
42.16 |
3.56 |
1.65 |
2.77 |
3.56 |
4.85 |
4.85 |
6.35 |
9.70 |
||||||
|
40 |
1 1/2” |
48.26 |
3.68 |
1.65 |
2.77 |
3.68 |
5.08 |
5.08 |
7.14 |
10.15 |
||||||
|
50 |
2” |
60.33 |
3.91 |
1.65 |
2.77 |
3.91 |
5.54 |
5.54 |
9.74 |
11.07 |
||||||
|
65 |
2 1/2” |
73.03 |
5.16 |
2.11 |
3.05 |
5.16 |
7.01 |
7.01 |
9.53 |
14.02 |
||||||
|
80 |
3” |
88.90 |
5.49 |
2.11 |
3.05 |
5.49 |
7.62 |
7.62 |
11.13 |
15.24 |
||||||
|
90 |
3 1/2” |
101.60 |
5.74 |
2.11 |
3.05 |
5.74 |
8.08 |
8.08 |
||||||||
|
100 |
4” |
114.30 |
6.02 |
2.11 |
3.05 |
6.02 |
8.56 |
8.56 |
11.12 |
13.49 |
17.12 |
|||||
|
125 |
5” |
141.30 |
6.55 |
2.77 |
3.40 |
6.55 |
9.53 |
9.53 |
12.70 |
15.88 |
19.05 |
|||||
|
150 |
6” |
168.27 |
7.11 |
2.77 |
3.40 |
7.11 |
10.97 |
10.97 |
14.27 |
18.26 |
21.95 |
|||||
|
200 |
8” |
219.08 |
8.18 |
2.77 |
3.76 |
6.35 |
8.18 |
10.31 |
12.70 |
12.70 |
15.09 |
19.26 |
20.62 |
23.01 |
22.23 |
|
|
250 |
10” |
273.05 |
9.27 |
3.40 |
4.19 |
6.35 |
9.27 |
12.70 |
12.70 |
15.09 |
19.26 |
21.44 |
25.40 |
28.58 |
25.40 |
|
|
300 |
12” |
323.85 |
9.53 |
3.96 |
4.57 |
6.35 |
10.31 |
14.27 |
12.70 |
17.48 |
21.44 |
25.40 |
28.58 |
33.32 |
25.40 |
|
|
350 |
14” |
355.60 |
9.53 |
3.96 |
4.78 |
6.35 |
7.92 |
11.13 |
15.09 |
12.70 |
19.05 |
23.83 |
27.79 |
31.75 |
35.71 |
|
|
400 |
16” |
406.40 |
9.53 |
4.19 |
4.78 |
6.35 |
7.92 |
12.70 |
16.66 |
12.70 |
21.44 |
26.19 |
30.96 |
36.53 |
40.49 |
|
|
450 |
18” |
457.20 |
9.53 |
4.19 |
4.78 |
6.35 |
7.92 |
14.27 |
19.05 |
12.70 |
23.83 |
29.36 |
34.93 |
39.67 |
45.24 |
|
|
500 |
20” |
508.00 |
9.53 |
4.78 |
5.54 |
6.35 |
9.53 |
15.09 |
20.62 |
12.70 |
26.19 |
32.54 |
38.10 |
44.45 |
50.01 |
|
|
550 |
22” |
558.80 |
9.53 |
4.78 |
5.54 |
6.35 |
9.53 |
22.23 |
12.70 |
28.58 |
34.93 |
41.28 |
47.63 |
53.98 |
||
|
600 |
24” |
609.60 |
9.53 |
5.54 |
6.35 |
6.35 |
9.53 |
17.48 |
24.61 |
12.70 |
30.96 |
38.89 |
46.02 |
52.37 |
59.54 |
|
|
650 |
26” |
660.40 |
9.53 |
7.92 |
12.70 |
12.70 |
||||||||||
|
700 |
28” |
711.20 |
9.53 |
7.92 |
12.70 |
12.70 |
||||||||||
|
750 |
30” |
762.00 |
9.53 |
6.35 |
7.92 |
7.92 |
12.70 |
12.70 |
||||||||
|
800 |
32” |
812.80 |
9.53 |
7.92 |
12.70 |
17.48 |
12.70 |
|||||||||
|
850 |
34” |
863.60 |
9.53 |
7.92 |
12.70 |
17.48 |
12.70 |
|||||||||
|
900 |
36” |
914.40 |
9.53 |
7.92 |
12.70 |
19.05 |
12.70 |
|||||||||
| DN 1000mm and above Diameter pipe wall thickness Maximum 25mm | ||||||||||||||||
Standard & Grade
|
Standard |
Steel Grades |
|
API 5L: Specification for Line Pipe |
GR.B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70, X80 |
|
ASTM A252: Standard Specification for Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Piles |
GR.1, GR.2, GR.3 |
|
EN 10219-1: Cold Formed Welded Structural Hollow Sections of Non-alloy and Fine Grain Steels |
S235JRH, S275J0H, S275J2H, S355J0H, S355J2H, S355K2H |
|
EN10210: Hot Finished Structural Hollow Sections of Non-Alloy and Fine Grain Steels |
S235JRH, S275J0H, S275J2H, S355J0H, S355J2H, S355K2H |
|
ASTM A53/A53M: Pipe, Steel, Black and Hot-Dipped, Zinc-Coated, Welded and Seamless |
GR.A, GR.B |
|
EN 10217: Welded Steel Tubes for Pressure Purposes |
P195TR1, P195TR2, P235TR1, P235TR2, P265TR1, P265TR2 |
|
DIN 2458: Welded Steel Pipes and Tubes |
St37.0, St44.0, St52.0 |
|
AS/NZS 1163: Australian/New Zealand Standard for Cold-formed Structural Steel Hollow Sections |
Grade C250 , Grade C350, Grade C450 |
|
GB/T 9711: Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries - Steel Pipe for Pipelines |
L175, L210, L245, L290, L320 , L360, L390 , L415, L450 , L485 |
|
AWWA C200: Steel Water Pipe 6 Inches (150 mm) and Larger |
Carbon Steel |
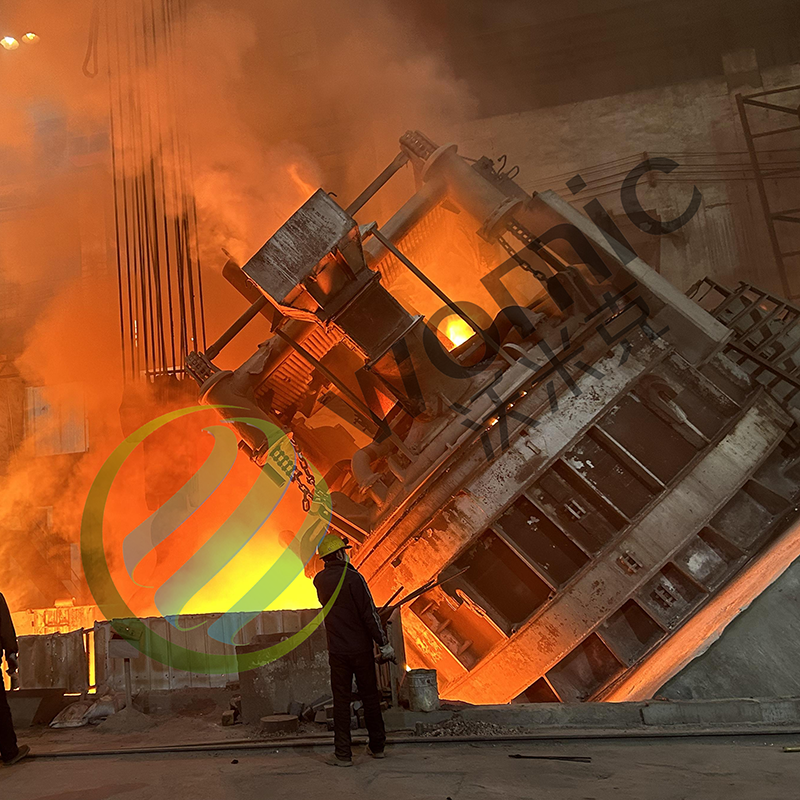
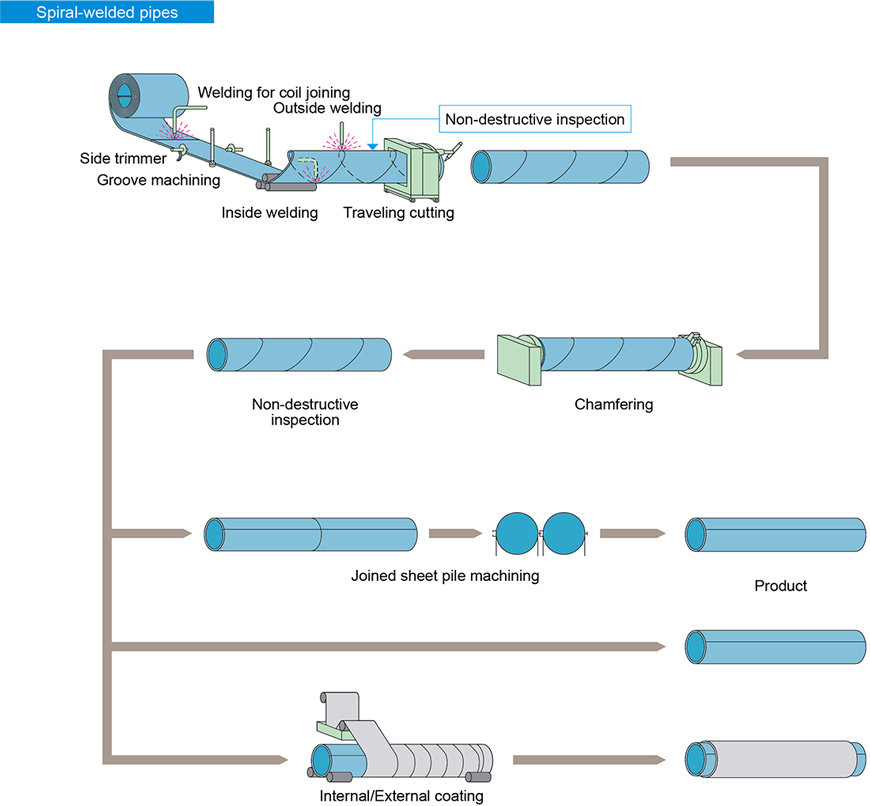
Manufacturing Process
Quality Control
● Raw Material Checking
● Chemical Analysis
● Mechanical Test
● Visual Inspection
● Dimension Check
● Bend Test
● Impact Test
● Intergranular Corrosion Test
● Non-Destructive Examination (UT, MT, PT)
● Welding Procedure Qualification
● Microstructure Analysis
● Flaring and Flattening Test
● Hardness Test
● Pressure Testing
● Metallography Testing
● Corrosion Testing
● Eddy Current Testing
● Painting and Coating Inspection
● Documentation Review
Usage & Application
Spiral steel pipes are versatile and widely used in various industries due to their unique characteristics and advantages. They are formed by helically welding steel strips together to create a pipe with a continuous spiral seam. Here are some common applications of spiral steel pipes:
● Fluid Transport: These pipes efficiently move water, oil, and gas across long distances in pipelines due to their seamless build and high strength.
● Oil and Gas: Vital for oil and gas industries, they transport crude oil, natural gas, and refined products, serving exploration and distribution needs.
● Piling: Foundation piles in construction projects support heavy loads in structures like buildings and bridges.
● Structural Use: Employed in building frameworks, columns, and supports, their durability contributes to structural stability.
● Culverts and Drainage: Used in water systems, their corrosion resistance and smooth interiors prevent clogging and enhance water flow.
● Mechanical Tubing: In manufacturing and agriculture, these pipes provide cost-effective, sturdy solutions for components.
● Marine and Offshore: For harsh environments, they're utilized in underwater pipelines, offshore platforms, and jetty construction.
● Mining: They convey materials and slurry in demanding mining operations due to their robust construction.
● Water Supply: Ideal for large-diameter pipelines in water systems, efficiently transporting significant water volumes.
● Geothermal Systems: Used in geothermal energy projects, they handle heat-resistant fluid transfer between reservoirs and power plants.
The versatile nature of spiral steel pipes, combined with their strength, durability, and adaptability, makes them an essential component across a wide range of industries and applications.
Packing & Shipping
Packing:
The packing process for spiral steel pipes involves several key steps to ensure the pipes are adequately protected during transportation and storage:
● Pipe Bundling: Spiral steel pipes are often bundled together using straps, steel bands, or other secure fastening methods. Bundling prevents individual pipes from moving or shifting within the packaging.
● Pipe End Protection: Plastic caps or protective covers are placed on both ends of the pipes to prevent damage to the pipe ends and the internal surface.
● Waterproofing: Pipes are wrapped with waterproof materials, such as plastic sheets or wrapping, to shield them from moisture during transportation, particularly in outdoor or maritime shipping.
● Padding: Additional padding materials, such as foam inserts or cushioning materials, might be added between the pipes or at vulnerable points to absorb shocks and vibrations.
● Labeling: Each bundle is labeled with important information, including pipe specifications, dimensions, quantity, and destination. This aids in easy identification and handling.
Shipping:
● Shipping spiral steel pipes requires careful planning to ensure safe and efficient transportation:
● Transport Mode: The choice of transport mode (road, rail, sea, or air) depends on factors like distance, urgency, and destination accessibility.
● Containerization: Pipes can be loaded into standard shipping containers or specialized flat-rack containers. Containerization protects the pipes from external elements and provides a controlled environment.
● Securing: Pipes are secured within containers using appropriate fastening methods, such as bracing, blocking, and lashing. This prevents movement and minimizes the risk of damage during transit.
● Documentation: Accurate documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and shipping manifests, is prepared for customs clearance and tracking purposes.
● Insurance: Cargo insurance is often obtained to cover potential losses or damages during transit.
● Monitoring: Throughout the shipping process, pipes may be tracked using GPS and tracking systems to ensure they are on the right route and schedule.
● Customs Clearance: Proper documentation is provided to facilitate smooth customs clearance at the destination port or border.
Conclusion:
Proper packing and shipping of spiral steel pipes are essential to maintain the pipes' quality and integrity during transportation. Following industry best practices ensures that the pipes reach their destination in optimal condition, ready for installation or further processing.
















